 |
Section One - Background:
Lesson 1-3: File Naming
Now that you understand the concept of file format,
let's discuss file naming.
Traditionally, (on MS-DOS systems) file names were limited to eight
characters.
File names could have fewer than eight characters, but not more. File names could also have a three
character extension,
separated from the name by a period (called a "dot").
The typical, traditional 8.3 file name looks like this:
filename.ext
The extension could be between one and three characters. File name extensions are often
used to identify the type of file. For example, Word files use the extension ".doc" which stands for
"Document", of course. Ichitaro files use ".jxw" or ".jsw". (Who knows what those two stand for!)
Common graphic file extensions are ".gif" and ".jpg" . Text files use the ".txt" extension,
and web page files use an ".htm" or ".html" extension.
The extension tells the computer what type of file it is, and what software program it should use to open it.
Did you know, that only Japanese computer systems can read Japanese kana/kanji file names?
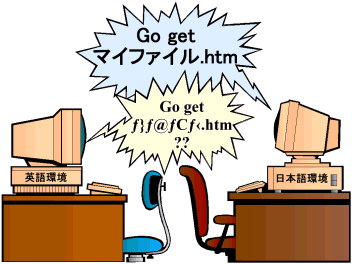 If you use kana or kanji in your file names, people outside of Japan will have trouble
with your pages, and may not be able to read them at all. On your own computer
it doesn't matter how you name your files. But when you put up pages on the Internet,
anyone from anywhere in the world should be able to look at your pages. Therefore, even if your pages
are written only in Japanese, you should still use only
single-byte
romaji or numbers in your file names.
If you use kana or kanji in your file names, people outside of Japan will have trouble
with your pages, and may not be able to read them at all. On your own computer
it doesn't matter how you name your files. But when you put up pages on the Internet,
anyone from anywhere in the world should be able to look at your pages. Therefore, even if your pages
are written only in Japanese, you should still use only
single-byte
romaji or numbers in your file names.
All web page files are actually text files, but they are a special type of text file.
Although you must save web pages as text files, you should not use the".txt" file name extension.
Rather, you should use the ".htm" (or ".html") extension.
Some software programs, including Notepad, will automatically add the ".txt" extension when you choose
the "text" file type from the drop-down list in the [Save As] dialog box.
If this happens, you must remove the ".txt" extension and replace it with the ".htm" extension.
Even if you do this, some software programs will still add another ".txt" extension to the end
of the file name the next time you save it. To stop Notepad from doing this:
- Open your file with Notepad.
- From the file menu, choose [Save as] / [名前を付けて保存].
- Change the File Type: from [text] to [All *.*]
- Change your file name extension from [.txt] to [.htm].
- Click [Save].
You only need to do this once. Any time you save your file after this, just use [Save] /
[上書き保存].
the [.htm] extension will be kept.
 Here are some basic rules for naming files for use on the Web:
Here are some basic rules for naming files for use on the Web:
Never use kana, kanji or any double-byte
(DOUBLEーbyte) characters in your file names.
Never use spaces in your file names.
Never use punctuation
marks ( ? : ; ! , etc.) except for the period just before the extension.
And, don't use any symbol characters ( * & § $ # etc.) except the underbar ( _ ) or the hyphen ( - ).
Here are some examples of good and bad file names:
| Good: |
No good: |
Reason: |
| mypage.htm |
my page.htm |
spaces are not permitted |
| whynot.htm |
why not?.htm |
spaces and punctuation marks are not permitted |
| lookhere.htm |
look*here*.htm |
symbol characters are not permitted |
| myfile.htm |
マイFILE名.htm |
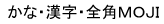 are not permitted are not permitted |
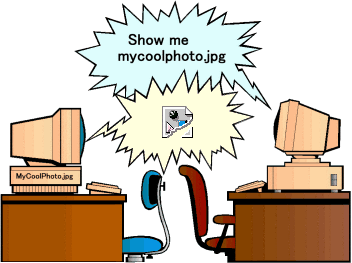 Case
is also important for files on the Internet. Most web servers run on UNIX or Linux,
which means UPPER CASE and lower case letters are clearly distinguished.
That means you must use case consistently. If you have a file named MyCoolPhoto.jpg,
and you put it on your page using the name MyCoolphoto.jpg, your image tag will not work.
The case must match exactly. Your best strategy,
is to always use only lower case file names.
Case
is also important for files on the Internet. Most web servers run on UNIX or Linux,
which means UPPER CASE and lower case letters are clearly distinguished.
That means you must use case consistently. If you have a file named MyCoolPhoto.jpg,
and you put it on your page using the name MyCoolphoto.jpg, your image tag will not work.
The case must match exactly. Your best strategy,
is to always use only lower case file names.
Review:
- File names usually contain a period, also called a "dot," followed by the extension.
- Extensions are usually three characters long.
- Extensions are often used to identify file types (formats).
- Web pages are special text files which use .htm (or .html) as the file name extension.
- Use only single-byte alphabet letters (romaji) or numbers for web page file names.
- Never use double-byte characters (kana, kanji, double-byte letters or numbers) spaces, punctuation marks, or other symbol characters in file names.
- Use case consistently.
|


 Case
is also important for files on the Internet. Most web servers run on UNIX or Linux,
which means UPPER CASE and lower case letters are clearly distinguished.
That means you must use case consistently. If you have a file named MyCoolPhoto.jpg,
and you put it on your page using the name MyCoolphoto.jpg, your image tag will not work.
The case must match exactly. Your best strategy,
is to always use only lower case file names.
Case
is also important for files on the Internet. Most web servers run on UNIX or Linux,
which means UPPER CASE and lower case letters are clearly distinguished.
That means you must use case consistently. If you have a file named MyCoolPhoto.jpg,
and you put it on your page using the name MyCoolphoto.jpg, your image tag will not work.
The case must match exactly. Your best strategy,
is to always use only lower case file names. If you use kana or kanji in your file names, people outside of Japan will have trouble
with your pages, and may not be able to read them at all. On your own computer
it doesn't matter how you name your files. But when you put up pages on the Internet,
anyone from anywhere in the world should be able to look at your pages. Therefore, even if your pages
are written only in Japanese, you should still use only
If you use kana or kanji in your file names, people outside of Japan will have trouble
with your pages, and may not be able to read them at all. On your own computer
it doesn't matter how you name your files. But when you put up pages on the Internet,
anyone from anywhere in the world should be able to look at your pages. Therefore, even if your pages
are written only in Japanese, you should still use only
 Here are some basic rules for naming files for use on the Web:
Here are some basic rules for naming files for use on the Web: